Introduction:
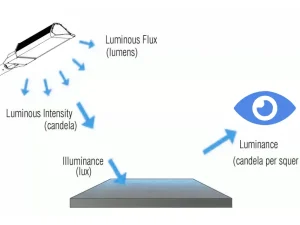
Understanding the relationship between watts, lumens, and lux is crucial in lighting. Watts measure the energy a light source consumes, while lumens indicate the amount of visible light emitted. On the other hand, Lux refers to the intensity of light that falls on a specific area. Converting watts to lumens helps determine how much light a fixture produces based on energy usage. Similarly, converting lumens to lux lets you know the lighting level in a given space. This guide explains how to convert watts to lumens, lumens to lux, and the factors influencing these conversions. You can get more light by improving luminous efficacy while using less energy.

What Are Watts?
Watts measure electrical power, or the rate at which energy is used. In lighting, watts show how much energy a bulb consumes per second. The more watts, the more energy the light source requires. For example, a 60-watt bulb uses 60 joules of energy every second. It is important to note that watts do not directly tell you how bright a light is. Depending on their efficiency, two bulbs with the same wattage can emit different light levels. Therefore, while watts show energy usage, they don’t represent the light output. In the case of LEDs, for instance, less energy (watts) can produce more light, making them more energy-efficient.
What Are Lumens?
Lumens measure the total amount of visible light emitted by a source. The higher the lumens, the brighter the light. When shopping for bulbs, lumens give a clearer idea of the light output instead of watts, indicating power consumption. For example, a 100-watt incandescent bulb typically produces about 1600 lumens, whereas an LED bulb of the same brightness may only consume 14 watts.
Understanding lumens helps choose bulbs for specific lighting needs, ensuring adequate illumination for various tasks. In short, lumens provide a direct measure of light, making it easier to compare different light sources. They help define the light’s effectiveness in a given space.
What Is Lux?
Lux is a unit of illuminance that measures how much light falls on a surface. It’s the result of dividing the total lumens by the illuminated area. Essentially, lux describes the concentration of light in a specific location. For example, if a 1000-lumen light source spreads over a 10-square-meter area, the illuminance is 100 lux.
The more concentrated the light, the higher the lux value. Unlike lumens, which describe the total light output, lux considers the area receiving the light. Understanding lux helps determine the adequacy of light in a room or space. Higher lux values are required for tasks like reading or working.
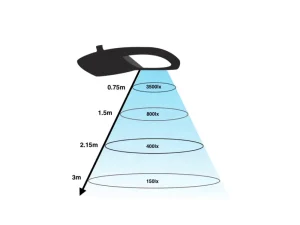
Difference Between Lumens and Lux
While lumens and lux relate to light, they are different. Lumens measure the total amount of visible light emitted by a source without considering the area it covers. Lux, on the other hand, measures how much light reaches a given area. For example, a bulb with 1000 lumens might create a different lux level depending on the room size.
The lux will be lower if the light source spreads over a large area. However, the lux will be higher if the light is focused on a small area. Therefore, while lumens focus on the amount of light produced, lux measures the intensity of light in a specific area.
How to Convert Watts to Lumens and Lumens to Lux?
To convert watts to lumens, you need to understand the light source’s luminous efficacy. Luminous efficacy refers to how well a light source converts electrical energy (watts) into visible light (lumens). For example, LEDs typically have an efficacy of around 80-100 lumens per watt, meaning a 10-watt LED bulb would produce 800-1000 lumens. However, this can vary depending on the type of light bulb, such as incandescent, halogen, or fluorescent.
Example: If you have a 10-watt LED bulb with 90 lumens per watt, the calculation would be 10 watts × 90 lumens/watt = 900 lumens. This means the LED bulb emits 900 lumens of light.
Convert Lumens to Lux:
To convert lumens to lux, you need to know the area over which the light is distributed. The formula for lux is:
Lux = Lumens / Area (in square meters)
For example, if you have 1000 lumens spread over 5 square meters, the calculation would be: 1000 lumens ÷ 5 m² = 200 lux. This means the light intensity on the surface is 200 lux.
How to Improve Luminous Efficacy?
Improving luminous efficacy means maximizing light output while minimizing energy consumption. Several factors influence the efficiency of lighting systems. These factors include color temperature (CCT), color rendering index (CRI), bins, heat dissipation, LED drivers, and lighting distribution.
1. CCT
Color Correlated Temperature (CCT) refers to the color of the light emitted by a light source, measured in Kelvin (K). A lower CCT (below 3000K) produces warm, yellow light, while a higher CCT (above 5000K) creates cool, blue light. The optimal CCT depends on the space’s lighting requirements. For example, cool white light is preferred for offices, while warm white is ideal for homes. Selecting the right CCT ensures better lighting effectiveness and enhances the space’s aesthetic.
2. CRI
Color Rendering Index (CRI) measures how accurately a light source shows the colors of objects compared to natural light. A CRI of 100 is considered perfect, meaning the colors appear exactly as they would under sunlight. Light sources with higher CRI values produce more natural-looking colors, which are essential in applications like art galleries or retail settings. Opt for light sources with higher CRI ratings to improve luminous efficacy, as they offer better color accuracy and more pleasant lighting.
3. Bins
LED bins categorize LEDs based on color, brightness, and performance characteristics. Different bins within a product series can exhibit slight variations in light output and color. Choosing LEDs from the same bin ensures consistency in brightness and color, especially in large installations.
High-quality manufacturers sort LEDs into bins to guarantee uniformity. When improving luminous efficacy, selecting LEDs within the same bin can optimize lighting performance and prevent variations in illumination levels or color temperature.
4. Heat Dissipation
Heat dissipation is a key factor in maintaining the efficiency and lifespan of light sources. Excessive heat can reduce a bulb’s luminous efficacy and cause premature failure. Good thermal management systems are essential for LEDs to function at peak efficiency. Heat sinks and heat-resistant materials play a key role. Proper heat dissipation keeps the light source cool and ensures efficient operation. This leads to increased energy savings and extends the product’s longevity. Enhanced thermal control improves lighting performance.
5. LED Driver
An LED driver regulates the electrical current supplied to the LED, ensuring stable performance. A high-quality LED driver helps maximize luminous efficacy. It controls power usage and prevents energy waste. The driver also protects the LED from voltage spikes. It ensures a consistent light output.
Choosing the right LED driver can improve efficiency. It enhances the performance of a lighting system. Ensure compatibility between the LED and driver. This ensures optimal light production and energy consumption. It leads to longer-lasting and efficient illumination.
6. Lighting Distribution
Lighting distribution refers to how light is spread across a given area. Proper distribution ensures that light is evenly spread and reaches all parts of the space. Specific lighting setups, such as spotlights or floodlights, sometimes focus light in a particular direction. Choosing the correct distribution pattern is essential for achieving the desired lighting effect. This factor can improve luminous efficacy by ensuring the light is used without creating unwanted dark spots or glare.
LED Watts to Lumens
When converting LED watts to lumens, you should consider the luminous efficacy of the LED. Generally, modern LEDs produce around 80-100 lumens per watt. To calculate the lumens produced by LED wattage, multiply the watts by the luminous efficacy. For example, a 15-watt
LED with an efficacy of 90 lumens per watt would produce 1350 lumens. The efficiency of LED technology allows for more light output per watt. This is compared to traditional bulbs like incandescent or fluorescent lights.
Conclusion
Converting watts to lumens and lumens to lux helps in understanding lighting efficiency. While watts measure energy consumption, lumens quantify the light output, and lux indicates the light intensity over a specific area. By converting watts to lumens, you can determine the brightness of light sources based on their energy consumption. Converting lumens to lux allows you to assess lighting levels in any space. Improving luminous efficacy involves several factors.
These include CCT, CRI, heat dissipation, and proper LED drivers. Each of these elements enhances lighting performance. They also help save energy. For businesses and homes, efficient LED lighting solutions are crucial. These solutions reduce energy costs. They also provide the proper illumination. Properly managing watts, lumens, and lux ensures optimal lighting for various applications.










